What is Electrical Wiring? Different Types, Advantages, Disadvantages and their Applications
What is Electrical Wiring? Different Types, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Their Applications
Welcome to the world of electrical wiring! It’s a fundamental aspect of our modern lives that often goes unnoticed, yet it powers our homes, businesses, and industries. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore electrical wiring, its various types, their advantages and disadvantages, and where they find application.
Introduction
Electrical wiring forms the nervous system running through any building or facility, enabling power distribution and lighting functionality. Properly installed electrical wiring is crucial for safe and efficient electrical operations. Let’s explore what electrical wiring is, the key types, sizing considerations, comparative advantages and disadvantages, and the diverse applications of electrical wiring.
What is Electrical Wiring?
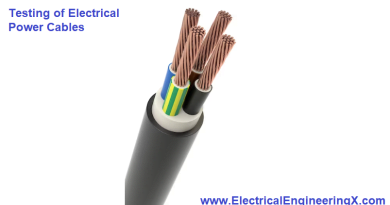
Electrical wiring refers to the interconnected cables and wires installed to distribute electricity from the supply source to end devices and equipment. It comprises insulated conductors like copper carrying current, supported and protected by conduits, cable trays, raceways, or insulation. Wiring connects devices in a building’s electrical system into circuits controlled by switches, breakers, and fuses.
Electrical wiring is the intricate network of conductive materials that transmit electrical power from a source to various devices and appliances within our homes, workplaces, and industrial settings. This fundamental component of our modern lives deserves closer examination, from its historical roots to the diverse types available today. In this article, we delve into electrical wiring, exploring its different types, their advantages and disadvantages, and where they find their most critical applications.
Importance of Electrical Wiring
Good quality electrical wiring is vital for:
- Enabling proper functioning of lighting, appliances, devices
- Preventing short circuits, fires, and electrocution hazards
- Minimizing power losses and voltage drops
- Future load expansions with sufficient capacity
- Interfacing electrical devices together safely
- Providing grounding paths and lightning protection
Basic Structure of Electrical Wiring
Electrical wiring typically contains:
- Conductors like copper to carry current flow
- Insulation like PVC around conductors for protection and isolation
- Outer jacket for enclosing the insulated wires
- Optional armor or shielding for mechanical strength
- Terminations like lugs or connectors to interface with devices
Now let’s discuss the major types of electrical wiring used in installations.
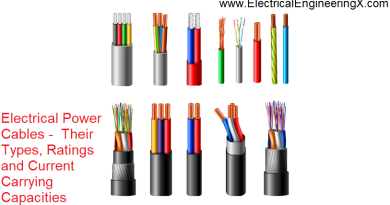
Types of Electrical Wiring
Electrical wiring types are categorized as:
Single-Strand Wiring
Have individual insulated solid or stranded conductors bundled together:
Solid Core Wiring
- Single solid metallic conductor
- Used for fixed installations in conduits
- Offers good conductivity but less flexibility
Stranded Wiring
- Multiple thin stranded wires bundled
- More flexible but lower conductivity
- Used where flexibility is needed
Multi-Strand Wiring
Have multiple insulated conductors pre-bundled together in a jacket:
Non-metallic Sheathed Cable
- Insulated wires bundled in a non-metallic PVC jacket
- Common residential branch circuit wiring
- Limited mechanical strength
Armored Cable
- Wires encased in a flexible metallic armor and outer jacket
- Used where mechanical protection is needed
- Good for damp areas
Flexible Metal Conduit
- Wires drawn through interlocked metal tubing
- High flexibility and mechanical strength
- Used for connections across moving parts
Proper sizing of wiring is crucial for electrical installations.
Electrical Wire Sizing
Key factors determine appropriate wire sizes:
Current Rating
Wire gauge was chosen such that rated current carrying capacity meets circuit current needs plus a safety margin.
Voltage Drop
Larger wire sizes minimize voltage drops over long cable runs.
Temperature Rating
Insulation is chosen based on maximum ambient temperatures.
Environmental Factors
Wiring designed to withstand environmental conditions like moisture, corrosive agents etc.
Different wiring types offer relative advantages:
Advantages of Different Wiring Types
Single-Strand Wiring Advantages
- The solid core has excellent conductivity
- Stranded provides flexibility
- Widely available and cost-effective
Multi-Strand Wiring Advantages
- Complete system with all conductors
- Simplified installation
- Armored and shielded types provide protection
- Specialized varieties suit unique needs
Wiring types also have certain limitations:
Disadvantages of Different Wiring Types
Single-Strand Wiring Disadvantages
- Manual intensive installation
- Multiple conductors increase large conduit needs
- Less protection from physical damage
Multi-Strand Wiring Disadvantages
- Prefabricated nature provides less customization
- Specialized types can be more expensive
- Faults require the replacement of the entire wiring
Electrical wiring finds wide-ranging applications across sectors:
Electrical Wiring Applications
Residential Wiring
Home electrical wiring distributes power across lighting, appliances, etc., following local codes using NM cables, conduit, armored cable, etc.
Commercial Wiring
In commercial settings like offices and malls, physical protection and high currents necessitate using heavy gauge THHN/THWN wires in conduit.
Industrial Wiring
Industrial facilities utilize cabling like TC, MC, or tray wiring to distribute heavy machinery across long distances and hazardous areas.
Specialty Wiring
Specialty wiring like shielded cable, instrumentation cable, heating cable, etc. serves unique functions across applications.
Applications of Electrical Wiring
Discover the diverse electrical wiring applications from residential to commercial and industrial settings.
Safety Considerations
Safety should always be a priority when dealing with electrical wiring. Learn essential safety tips and precautions.
Maintenance and Upgrades
Find out how to maintain your electrical wiring and when it might be time for an upgrade.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrical wiring is the lifeline of our modern world. Understanding its types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications is crucial for safe and efficient electrical systems.
Summary
Electrical wiring provides the vital physical infrastructure for electricity distribution across sectors. Key considerations include wiring types, sizing, DERATING factors, and installation methods dictated by the operating environment. While single-strand wiring offers basic function, multi-strand varieties with sheathing and insulation enhance protection and safety. Advancements in wiring continue to drive efficiency, safety, and reliability across electrical installations.
FAQs
- What main components comprise electrical wiring?
Electrical wiring contains conductors like copper, insulation around conductors, outer protective jackets or sheathing, terminations, and connectors.
- What factors determine appropriate wire sizing?
Current rating, voltage drops, temperature, environment, and future capacity growth determine optimal electrical wire sizes.
- What are the types of single-strand electrical wiring?
Single-strand wiring includes solid core wiring and stranded wiring, which contain individual insulated conductors bundled together.
- What are examples of multi-strand electrical wiring types?
Multi-strand wiring includes armored cable, non-metallic sheathed cable, flexible metal conduit, and specialized cabling.
- What are the applications of electrical wiring?
Major applications include residential, commercial, and industrial lighting and power distribution facilities. Specialty wiring serves specific functions.
- What are the advantages of armored cable wiring?
Armored cables provide good physical protection, durability, and ease of handling for electrical wiring applications.
- When is metallic conduit wiring preferable?
Metallic conduits offer robust mechanical strength and protection suitable for industrial wiring applications.
- What are stranded wires used for in electrical systems?
Stranded wiring provides good flexibility and resistance to repeated bending, making it suitable for connections across moving parts.
- Why is larger wire sizing preferred generally?
Larger wiring minimizes voltage drops across long cable runs and provides higher current ratings to accommodate future load expansions.
- How does improper wire sizing impact electrical systems?
Undersized wires lead to excessive voltage drops, power losses, and possible insulation damage or fires due to overheating.