How to Install a Home Energy Storage System
Outline:
- Introduction to Home Energy Storage Systems
- What is a home energy storage system?
- How does it work?
- Benefits
- Determine if You Need a Home Energy Storage System
- Do you have solar panels?
- What are your energy needs and costs?
- Backup power considerations
- Choose the Right Battery Chemistry
- Lithium-ion vs lead-acid
- Power vs energy density
- Lifespan and maintenance
- Calculate the Right Storage Capacity
- Daily energy use
- Future energy needs
- Number of electric devices
- Select an Inverter System
- Standalone vs hybrid
- Power handling
- Efficiency and features
- Determine the Best Location
- Temperature control
- Ventilation
- Accessibility
- Understand Electrical Panel and Home Wiring Requirements
- Research Permits and Codes for Your Area
- Work with an Installer or Install It Yourself
- Pros and cons of DIY
- Saving on labor costs
- Purchase Equipment and Get Quotes from Installers
- Prepare Your Home for the Installation
- Install the Mounting Bracket and Shelving
- Mount and Connect the Batteries
- Install the Inverter System
- Perform Final Safety Checks and Power Up
How to Install a Home Energy Storage System
Installing an energy storage system in your home allows capturing electricity from solar panels or the grid to use later when you need it most. Home energy storage provides backup power, reduces electricity costs, and enables greater renewable energy self-sufficiency. This guide will review the major steps in adding battery storage to your home.
Introduction to Home Energy Storage Systems
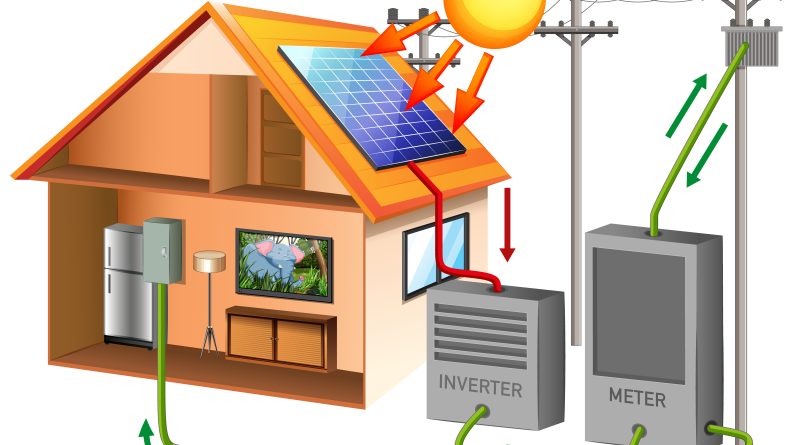
A home energy storage system consists of rechargeable batteries that can store excess electricity generated by rooftop solar panels or drawn from the grid during off-peak hours when rates are lower. The stored electricity can then be used to power your home during more expensive peak demand times or during grid outages.
Key components include the battery units, an inverter system, and monitoring/control systems. The batteries chemically store energy the inverter converts into usable AC electricity for your home. Controls manage the charging and discharging.
Benefits of adding home energy storage include:
- Backup power during utility grid outages
- Reduced electricity costs by optimizing usage
- Increased renewable energy self-sufficiency
- A smaller carbon footprint
Determine if You Need a Home Energy Storage System
There are a few key factors that will determine if a home battery system makes sense for your situation:
Do You Have Solar Panels?
If your home already has a rooftop solar PV system, adding storage allows capturing excess solar generation during the day to use at night when solar is unavailable. This also minimizes exporting unused solar energy.
What Are Your Energy Needs and Costs?
Analyze your monthly energy consumption and costs. Installing an extensive enough battery system to impact your electricity bills significantly requires careful projection of needs and savings.
Backup Power Considerations
If you want emergency backup capability during grid outages, size your system to cover critical loads. Prioritize necessities like refrigeration, lighting, healthcare devices, and phone charging.
Choose the Right Battery Chemistry
Two primary battery types are used for home energy storage:
Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Higher energy density allows more capacity in less space
- More lifespan cycles before replacement compared to lead-acid
- Costs more initially but lasts longer
Lead-Acid Batteries
- Inexpensive option good for shorter backup needs
- Lower energy density requires more space
- Shorter lifespan with fewer cycles before replacement
Also, consider power density. Lithium-ion offers both high power and energy density. Lead-acid has a lower power density.
Calculate the Right Storage Capacity
Your battery bank’s energy storage capacity must align with your household electricity requirements. Consider:
Daily Energy Use
Estimate your average daily energy consumption. Up to three days of storage is common for backup needs.
Future Energy Needs
Account for EV charging, electrification, or home expansions that may increase future demand.
Number of Electric Devices
The more devices needing backup power, the greater your capacity requirements will be.
Work with an installer to accurately size your system based on these variables. Undersizing will provide inadequate backup and savings. Oversizing adds unnecessary expense.
Select an Inverter System
The inverter converts DC electricity from the battery into usable AC power. Choose based on:
Standalone vs Hybrid Inverters
A standalone inverter operates independently from the grid. A hybrid inverter can integrate with the grid and solar system.
Power Handling
Ensure the inverter is rated for your load power demands and expected battery output.
Efficiency and Features
Compare efficiency ratings and functionality like app monitoring, auto adjustments, and battery optimization.
Determine the Best Location
Placement is important for optimal performance and lifespan of batteries. Ideal location has:
Temperature Control
Heat shortens battery life. A climate-controlled basement or garage works well if scorching/cold outdoor temperatures are avoided.
Ventilation
Batteries can release harmful gases. Allow air flow for ventilation without excessive dust or humidity.
Accessibility
Keep the units accessible for periodic maintenance while away from unauthorized access.
Understand Electrical Panel and Home Wiring Requirements
Your existing electrical panel must be able to manage the additional loads imposed by the storage system’s inverter and controls. Upgrading the panel may be needed.
Wiring from the batteries to the inverter and your panel must meet ampacity and voltage drop requirements. Your installer will handle panel integration.
Research Permits and Codes for Your Area
Most localities require getting permits for home energy storage installations. Research local zoning laws, HOA rules, utility company requirements, and fire & electric codes to ensure compliance.
Work with an Installer or Install It Yourself
Professional installation is recommended for the safety and correct integration your home’s electrical system. But a DIY installation is possible with ample skills.
Pros of Hiring an Installer
- Expertise in optimal configuration and safe practices
- Licensed and insured
- Saves significant time and effort
Pros of DIY Installation
- Cost savings on labor
- Learning experience and satisfaction
- More control over the project
Either route requires research and preparation. Weigh the options based on your specific situation.
Purchase Equipment and Get Quotes from Installers
Once you’ve made technical decisions on your system components and discussed permits/codes with local authorities, it’s time to purchase equipment and get installation quotes:
- Order batteries, inverter, brackets/enclosures, disconnects, conduits, and wiring.
- Get 2-3 written quotes from licensed installers, including expected timeline, warranty, etc.
- Compare options and select the optimal installer with demonstrated expertise.
Prepare Your Home for the Installation
To get your home ready for the installation:
- Declutter the installation location and surrounding areas for easy access.
- Plan for heavy equipment that may need to be lifted/lowered during the process.
- Read up on the installation plan, so you know what to expect.
- Fully charge battery packs before installation day.
Install the Mounting Bracket and Shelving
The battery units need a sturdy base for support. Bolting the mounting bracket into the wall/floor and assembling the shelves or racking provides a stable foundation.
Mount and Connect the Batteries
With the base ready, the battery modules can be put into place. Each unit gets securely bolted to the racking and wired together to complete the battery bank circuit.
Install the Inverter System
The inverter also gets mounted and connected to the batteries and home electrical panel. Overcurrent protection devices and disconnects will be added for safety.
Perform Final Safety Checks and Power Up
Before start-up, all connections must be triple-checked for tightness and polarity. Provide oversight of these critical safety steps before the system goes live.
With those major steps complete, your home has a functioning energy storage system ready to save money and provide backup assurance! Be sure to test functionality and train all household members on emergency use procedures.
You’re now equipped to harness the power of renewable energy storage. Contact our team of installers to make your project a success!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the maintenance needs of home energy storage systems?
Maintenance is minimal, but batteries should be inspected for damage or issues periodically. Some systems may require cooling fan filters to be cleaned. Proper ventilation and temperature regulation help minimize required maintenance.
What certifications should qualified installers have?
Look for licensed electricians with training credentials from reputable institutions like the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP). Many manufacturers only authorize installers certified for their products.
How long do home battery systems typically last?
With proper operation and maintenance, the expected lifespan is 5-15 years, depending on battery chemistry, usage patterns, and environmental factors. Lithium-ion batteries generally last 8-15 years. Lead-acid may need replacement after 3-5 years.
Can I install batteries myself without electrical knowledge/experience?
It is not advisable for safety and proper system operation. Comprehensive DIY guides are available, but incorrect wiring can risk equipment damage or personal injury. Hiring a professional is highly recommended.
How much maintenance downtime is required?
Minimal downtime is expected for home energy storage systems. However, several hours may be needed periodically for software updates or filter replacements. Plan around critical backup needs.