A detailed Guide to Different Types of Lamps – their Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications
A detailed Guide to Different Types of Lamps and their Applications
Introduction
Lamps or light bulbs comprise an essential element of lighting and illumination systems. Various lamp technologies provide different functionality, efficiency, lifespan, and capabilities. Let’s explore what lamps are, the working principle and characteristics of key lights like incandescent, LED, CFL, HID, halogen, neon, etc., and their diverse applications.
What are Lamps?
Lamps, commonly known as light bulbs, are lighting devices that produce visible light by converting electrical energy into light using principles like incandescence, gas discharge, electroluminescence, etc. They contain a transparent glass bulb, lighting element, metal base, internal gases, and terminals.
History of Lighting
Early lamps used combustible materials like candles and oil. The invention of incandescent bulbs by Edison in 1879 revolutionized lighting. Fluorescent, HID, and LED lamps followed. Currently, LED and CFL lamps dominate energy-efficient lighting.
Lamp Basics
Key lamp performance parameters are luminous efficacy, color temperature, color rendering index (CRI), rated lifetime, and beam angle. Lamp designs vary among base types, voltage ratings, shapes, and sizes.

Different Types of Light Lamps and their Applications
| Lamp Type | Definition | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incandescent Lamp | Generates light by heating a filament wire until it emits visible light. | Warm, inviting glow. | Inefficient, short lifespan. | Ambient lighting in homes hospitality settings. |
| Fluorescent Lamp | Produces light by exciting mercury vapor to create ultraviolet light, stimulating phosphorescent coating to emit visible light. | Energy-efficient, long lifespan. | Contains mercury, flickering at times. | Commercial and industrial lighting, schools, and offices. |
| Compact Fluorescent Lamp | A compact version of fluorescent lamps known for energy efficiency and longevity. | Energy efficiency lasts longer than incandescent. | Contains mercury, initial cost. | Residential and commercial lighting, task lighting. |
| Light Emitting Diode (LED) | Generates light by passing an electric current through a semiconductor material. | Highly energy-efficient, long lifespan. | Initial cost, sensitive to heat. | Residential lighting, outdoor lighting, and automotive lighting. |
| Halogen Lamp | It contains a halogen gas and produces intense, white light. | Bright, white light, a longer lifespan than incandescents. | Generates heat, energy-inefficient. | Track lighting, under-cabinet lighting, automotive headlights. |
| High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Lamp | It uses gas and metal salts to produce high-intensity light. | Extremely bright, long lifespan. | Requires warm-up time, which can be expensive. | Streetlights, stadium lighting, automotive headlights. |
| Specialty Lamps | Designed for specific purposes, such as UV lamps for sterilization, grow lights for plants, and infrared lamps for heating. | Tailored for unique needs. | Limited versatility, specialized use cases. | Healthcare, horticulture, industrial process |
Now, let’s look at various lamp types in detail.
Incandescent Lamps
Working Principle
An electric current heats a tungsten filament wire to incandescence-producing light.
Types
Common varieties are general service, reflectors, globes, candles, and decorative bulbs.
Applications
Traditionally used for general lighting but being phased out. It is still found in specialty appliances.
Advantages
- Very inexpensive
- Excellent CRI of 100
Disadvantages
- Very low efficacy of 10-18 lumens/watt
- Short lifespan of 1000 hours
- Fragile filaments
LED Lamps
Working Principle
Light emission in semiconductor diode junctions when current flows.
Types
MR16, PAR, bulbs, tubes, panels, downlights, etc.
Applications
Widespread usage for home, commercial, industrial, and automotive lighting.
Advantages
- Very high efficacy of over 100 lumens/watt
- Long lifespan of 25,000+ hours
- Low-voltage DC operation
Disadvantages
- Higher initial costs
- Sensitive to overheating
- Lower CRI around 80 typically
CFL Lamps
Working Principle
Arc discharge excites mercury vapor, emitting UV light that phosphors convert to visible light.
Types
Some common shapes include spirals, globes, spots, reflectors, and tubulars.
Applications
Used for household lighting, offices, stores, street lighting, etc.
Advantages
- High efficacy around 60 lumens/watt
- Longer lifespan than incandescent
- Low power consumption
Disadvantages
- Contains mercury requiring special disposal
- Larger size than incandescent for the same brightness
- Slow-starting and dimming issues
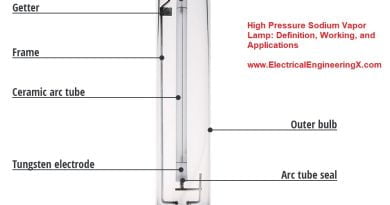
HID Lamps
Working Principle
Arc discharge between two electrodes vaporizes metals like mercury, sodium, and metal halides emitting light.
Types
Major types are mercury vapor, metal halide, and high/low-pressure sodium lamps.
Applications
Outdoor lighting, industrial buildings, warehouses, roadway lighting, etc. need high brightness.
Advantages
- Very high efficacy of 80-140 lumens/watt
- High-intensity light output
- Long operating life
Disadvantages
- Require ballasts
- Slow restart and re-striking issues
- Mercury disposal concerns
Halogen Lamps
Working Principle
Tungsten filament bulb with halogen gas allows redepositing of evaporated tungsten back, prolonging life.
Types
Available as bulbs, floodlights, spotlights, headlights, etc., in different wattages and beam patterns.
Applications
Traditionally used where high brightness in compact size needed – downlights, projectors, vehicle lights, etc. Now being replaced by LED.
Advantages
- Small size intensity in bulbs above 30 watts
- Good efficacy around 20 lumens/watt
- Low cost
Disadvantages
- Still lower lifespan and efficacy than LED and CFL
- Generates considerable heat.
Neon Lamps
Working Principle
Light emitted by neon or other noble gases ionized in a sealed glass tube.
Types
Tube lighting, indicator lamps, decorative lighting, channel letter lighting, etc.
Applications
Due to neon’s distinct bright red emission, signage, displays, and commercial decoration.
Advantages
- Attractive illumination
- Ultra-long lifespan of up to 25 years
- High voltage operation
Disadvantages
- Low luminous efficacy
- Large size requirements
- High operating voltages
Beyond the major categories, some specialty lamp types include:
Specialty Lamps
Germicidal Lamps
Emit UV radiation to sterilize and disinfect surfaces, air, and water.
Grow Lamps
Produce wavelengths optimized for plant growth applications.
Infrared Lamps
Generate infrared radiation used in heating and industrial processes.
Digital Projector Lamps
Specialized high-intensity arc lamps for image projection in LCD and DLP projectors.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
The Green Light
Energy-efficient lamps like CFLs and LEDs save on electricity bills and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Reducing Environmental Impact
Proper lamp disposal and recycling help minimize environmental impact, especially for lamps containing hazardous materials like mercury.
Maintenance and Safety
Keeping the Light Alive
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and replacing lamps, ensures consistent and safe lighting.
Safety Precautions
Practicing safety, including proper lamp handling and disposal, prevents accidents and environmental contamination.
Summary
Various lamp technologies provide customized visible or non-visible radiation for diverse lighting and heating needs. Selecting suitable lamps requires weighing factors like efficiency, intensity, size, lifespan, emission characteristics, and costs based on applications. Advances in LED and novel lamp technologies continue to disrupt century-old lighting paradigms.
FAQs
- What are the main components of an electric lamp?
Key parts are a glass bulb, lighting filament/element, metal base, internal gases, and electrical terminals.
- What are the different types of electric lamps?
Major varieties include incandescent, LED, CFL, HID, halogen, neon, germicidal, blacklight, and grow light, among many other lamps.
- What factors differentiate lamp performance?
Key factors are luminous efficacy, color temperature, CRI index, rated lifetime, beam angle/distribution and intensity.
- What are the main advantages of LED lamps?
Benefits of LED lamps include high energy efficiency, long life, low voltage operation, compactness and low maintenance.
- Where are CFL lamps commonly used?
For general area lighting applications, CFLs are used extensively in homes, offices, stores, etc.
- Why are HID lamps suitable for outdoor lighting?
The high intensity, high luminous efficacy, and long life make HID lamps advantageous for street, parking, stadium lighting, etc.
- What applications use halogen lamps?
Halogen lamps are still found in downlights, headlights, and projectors where small high-intensity beams are needed.
- How does a fluorescent lamp produce light?
It uses a gas discharge arc to excite mercury vapor that emits UV, which is converted to visible light by the phosphor coating.
- What are the main advantages of LED lighting?
LEDs offer extremely high energy efficiency, long life, durability, excellent color control, and low voltage operation.
- How does incandescent lamp lighting work?
Incandescent lamps produce light by heating a tungsten filament wire to high temperatures until it emits light.
MCQs
- What is the most energy-efficient type of lamp?
- LED lamps are currently the most energy-efficient type of lamp.
- Can LED lamps be used in outdoor applications?
- Yes, LED lamps are suitable for outdoor lighting due to their durability and energy efficiency.
- Are incandescent lamps still available in the market?
- Incandescent lamps are less common but can still be found for specific applications.
- What are the advantages of fluorescent lamps?
- Fluorescent lamps are energy-efficient and provide even lighting, making them suitable for various settings.
- How do halogen lamps differ from incandescent lamps?
- Halogen lamps are incandescent lamps that produce intense white light and have a longer lifespan.
- Are there any safety concerns with CFLs?
- CFLs contain a small amount of mercury, so proper disposal is essential to avoid environmental contamination.
- What is the lifespan of LED lamps?
- LED lamps can have a lifespan of up to 25,000 hours or more.
- Can HID lamps be used in residential lighting?
- HID lamps are typically used for industrial and outdoor lighting due to their brightness.
- Are specialty lamps cost-effective for niche applications?
- Specialty lamps offer specific benefits for unique needs and can be cost-effective in those contexts.
- How can I dispose of old lamps responsibly?
- To dispose of lamps responsibly, check local recycling programs or hazardous waste disposal facilities to ensure proper handling of lamps containing hazardous materials.