High Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp: Definition, Working, and Applications
High Pressure Sodium Vapor Lamp: Definition, Working, and Applications
Introduction
High-pressure sodium (HPS) lamps are highly efficient gas-discharge light sources that emit a characteristic monochromatic orange-yellow light. They are widely used for outdoor lighting applications requiring high-intensity illumination over large areas. Let’s explore the working principle, characteristics, types, pros/cons, and usage applications of high-pressure sodium vapor lamps.
What is a High Pressure Sodium Lamp?
A high-pressure sodium lamp is a specialized gas discharge lamp containing sodium metal vapor operating at high pressures that produces light by the excitation of sodium ions. They provide high luminous efficacy and long life, making them suitable for street lighting, floodlighting, etc.
History of HPS Lamps
General lighting engineers developed and commercialized high-pressure sodium lamps in the 1960s as an efficient alternative to earlier mercury vapor lamps. Their orange-pink monochromatic light proved effective in foggy conditions.
Components of HPS Lamps
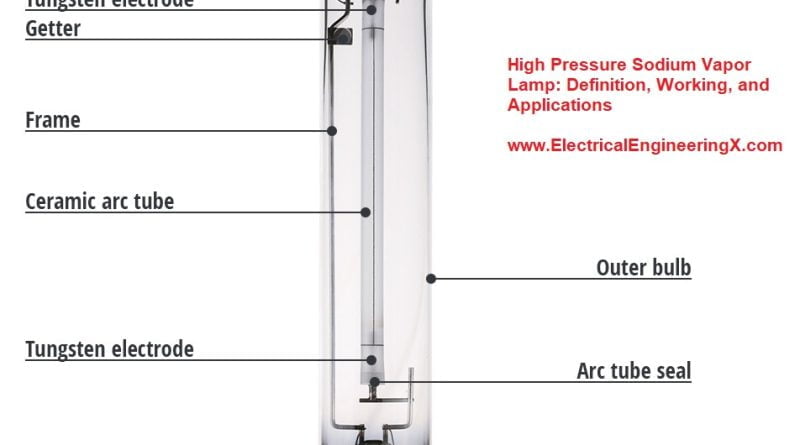
The major components are a borosilicate glass bulb containing sodium, mercury, and xenon gas fill along with a pair of closed-coiled tungsten electrodes. The bulb is coated inside with phosphors.

Now, let’s understand how HPS lamps produce light.
Working Principle of HPS Lamps
Gas Discharge Principle
Electric current flowing between the electrodes excites the gas mixture, causing it to emit radiation, primarily as invisible ultraviolet rays.
Voltage Ionization
An initial high-voltage pulse applied via the ballast ionizes the gas mixture, allowing current to flow easily.
Sodium Vapor Light Production
The phosphor coating absorbs ultraviolet radiation and re-emits it as visible orange-yellow sodium vapor spectrum light.
Use of Ballasts
Integrated magnetic or electronic ballasts provide the high starting voltages and current limiting required for stable arc discharge.
The Glow of Efficiency: How Do HPS Lamps Work?
Sodium and Mercury: The Chemistry of Light
At the heart of an HPS lamp lies a mix of sodium and mercury, which, when energized, produce the characteristic yellowish glow. We’ll explore this chemical reaction in detail.
Starting the Illumination: Ignition and Operation
Discover how HPS lamps ignite and maintain illumination, ensuring consistent and reliable lighting.
The Warm Glow: Color Temperature of HPS Lamps
The color temperature of lighting is a critical factor, impacting visibility and ambiance. We’ll delve into the warm glow of HPS lamps and how it compare to other lighting options.
The light from HPS lamps has unique characteristics:
Characteristics of HPS Lamps
High Luminous Efficacy
Very high efficacy with values between 80-150 lumens/watts is possible owing to sodium’s excellent radiation efficiency when excited.
Lamp Lifetime
The rated average lifetime is 24,000 hours, with lumen depreciation of around 10-15% towards the end of life.
Color Properties
Orange-pink appearance with a low color temperature of around 2100K and poor color rendering index of 25 CRI.
Light Distribution
Directional floodlighting requires external reflectors or lenses to spread light for street lighting.
There are a few varieties of high-pressure sodium lamps:
Types of HPS Lamps
Standard HPS Lamps
Common type with characteristic monochromatic orange-yellow light and low CRI. Available from 35W to 1000W.
Deluxe HPS Lamps
Use special phosphors for slightly improved 70 CRI and color temperature of 2700K.
White SON Lamps
Employ multiple phosphor coatings to improve color appearance closer to daylight at 3000K and 80 CRI.
HPS Lamp Shapes
Standard bulbs, floodlighting tubes, and smaller elliptical or compact arc tube lamps exist based on lighting application needs.
Major advantages of HPS lamps:
Advantages of HPS Lamps
High Luminous Efficacy
Very high efficacy exceeding 100 lumens/Watt enables high-intensity lighting from lower wattages.
Long Working Life
A typical lifespan of over 20,000 hours reduces maintenance costs. Allows long interval lamp replacement cycles.
Good Color Rendition
Though monochromatic, the orange-yellow hue provides reasonably good color recognition at night.
Compact Size Options
Smaller lamp sizes yield high-intensity narrow spotlighting from smaller luminaires.
Dimmability
Light output can be continuously controlled or dimmed, unlike fluorescent lamps.
Some inherent limitations exist:
Limitations of HPS Lamps
Slow Restart and Warm-up
Up to 10 minutes to fully light up if power is disrupted due to gas pressure stabilization needs.
Requires Ballasts
Complex heavy inductive ballasts are needed to provide high starting voltages and control lamp operation.
Mercury Content
Contains some mercury, requiring responsible disposal and recycling.
Monochromatic Light
The deeply saturated narrow spectrum light has a CRI typically below 25 with visible color distortions.
Common usage scenarios benefiting from HPS lamp properties:
Applications of High-Pressure Sodium Lamps
Street Lighting
The high intensity, efficacy, and reasonably good visibility make HPS ideal for street, road, and public area lighting.
Parking Lot Lighting
Provides uniform and high-lumen density illumination over large uncovered parking lot areas through the night.
Floodlighting
Their narrow spot beam profile makes HPS suitable for area floodlighting of commercial and security zones while minimizing light trespass.
High Bay Lighting
Fixtures mounted at great heights efficiently illuminate large indoor industrial spaces, warehouses etc.
Tunnel Lighting
Long, thin, tubular HPS lamps help illuminate tunnels, underpasses, and low clearance areas under bridges, etc.
Comparisons with Other Lamp Types
- HPS has higher luminous efficacy and longer life than fluorescent and incandescent lamps.
- It is more suitable for high ceiling and outdoor lighting than LEDs presently.
- Light color is more acceptable at night than low-pressure sodium monochromatic yellow lamps.
- Lacks the full spectrum visual clarity of white light metal halide lamps.
Summary
High-pressure sodium lamps provide highly efficient and economical lighting solutions where visual needs are limited and high-intensity illumination is required over large areas through their narrowly radiating orange-yellow light. Advancements in color rendition and integrated control features continue to expand high-pressure sodium lighting capabilities while competing with LEDs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
FAQ 1: How do HPS lamps produce light?
HPS lamps produce light through the excitation of sodium and mercury vapor within the lamp, resulting in a characteristic yellowish glow.
FAQ 2: Are HPS lamps energy-efficient?
HPS lamps are relatively energy-efficient compared to older technologies but are less efficient than modern options like LEDs.
FAQ 3: Can HPS lamps be used for indoor lighting?
While HPS lamps are primarily designed for outdoor use, they can be used for indoor lighting in specific applications.
FAQ 4: What is the lifespan of an HPS lamp?
HPS lamps typically have a long lifespan, often ranging from 10,000 to 24,000 hours of use.
FAQ 5: Are there any environmental concerns with HPS lamps?
HPS lamps contain small amounts of mercury, which raises environmental concerns. Proper disposal is essential.
FAQ 6: Can HPS lamps be dimmed?
Yes, HPS lamps can be dimmed, but the process is more complex than dimming some other types of lamps.
FAQ 7: Are HPS lamps still widely used?
While newer technologies like LEDs have gained popularity, HPS lamps are still used in various applications, particularly in street lighting.
FAQ 8: How do HPS lamps compare to LED lighting?
HPS lamps are less energy-efficient and have a lower color rendering index than LED lighting, which is more efficient and versatile.
FAQ 9: Can HPS lamps be recycled?
Yes, HPS lamps can be recycled. Many regions have recycling programs for these lamps to handle their mercury content properly.
FAQ 10: Are there any safety precautions for handling HPS lamps?
Handling HPS lamps, especially when replacing them, requires care due to their fragile nature and the presence of mercury. Proper safety measures should be followed.
MCQs
- What is the working principle of high-pressure sodium lamps?
Electric discharge excites sodium vapor, which emits UV radiation converted to visible orange light by the phosphor coating.
- What are the key advantages of HPS lamps?
Major benefits are very high luminous efficacy, long lifetimes, reasonably good color recognition at night, and high-intensity spotlighting ability.
- Where are high-pressure sodium lamps commonly used?
Typical applications include street lighting, parking lot lighting, area floodlighting, high bay lighting, and tunnel illumination.
- Why is the light output of HPS lamps monochromatic?
It is due to the narrow band emission spectrum of excited sodium vapor at 589 nm wavelength producing its characteristic orange-yellow hue.
- What causes the long lifetime of HPS lamps?
Low electrode deterioration due to optimized thermal design and minimal sodium loss through amalgam containment allow long life.
- How does an HPS lamp produce such high luminous efficacy?
The radiation from sodium vapor is very efficiently converted to visible light compared to other gas discharges, resulting in high lumens per watt.
- What are some disadvantages of HPS lamps?
Drawbacks include slow starting, ballast needs, poor color rendition and illumination, and mercury content.
- Why are ballasts needed in HPS lamps?
Ballasts provide a high starting voltage to ionize the gas and limit current during stability operation.
- How does an HPS lamp differ from an LPS lamp?
HPS lamps operate at higher pressures, producing orange-yellow light rather than low-pressure LPS lamps emitting monochromatic yellow light.
- How does the performance of HPS lamps compare with LEDs?
While LEDs offer superior color qualities, HPS lamps can provide very high-intensity narrow spot illumination from smaller sizes.